What is Hyperforce?
Hyperforce is a new infrastructure architecture introduced by Salesforce that unifies the foundation of different Salesforce Clouds. It allows for Salesforce instances to be deployed over public clouds like (AWS, Azure and GCP). By leveraging public cloud partners Salesforce is able to expand quickly into newer regions and help clients with data residency and compliance requirements.
Some of the key features of Hyperforce are:
- Local data storage will be available for compliance and regulation.
- Every Salesforce app, customization and integration will be on Hyperforce and backwards compatible.
- Hyperforce has encryption at rest and in transit.
- For multi-cloud implementations, it provides the ability to separate the infrastructure from the application. Enabling the application infrastructure to be located closer to the client applications and users.
- Proximity – As a customer if you are already running your workloads in public data clouds, then combining salesforce data with existing workloads or using external processing capabilities like Salesforce Functions, or bridging Salesforce data with different application using MuleSoft. It leads to distinct advantages if Salesforce data is residing in the same public cloud instance.
Hyperforce Architecture
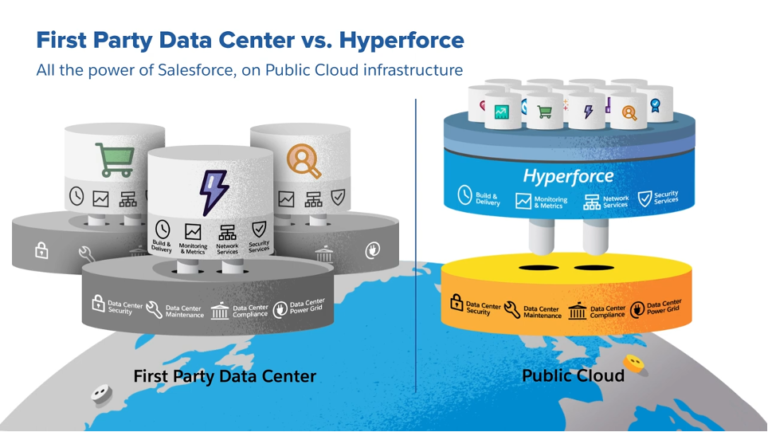
Hyperforce is a new infrastructure model, while the underlying physical layer of Hyperforce is managed by the public cloud providers, The core infrastructure that enables Lightning Platform over public cloud infrastructure is managed by Salesforce.
The key architectural principles of Hypeforce are:
Immutable Infrastructure
All infrastructure in Hyperforce is immutable. It means all the server, containers or VMs are created only once, if any patch or configuration update to the infrastructure is required. Then a new version is put up and the old version is pulled down. It enables predictable state without any configuration drift.
Infrastructure in public cloud can be expanded or reduced dynamically, Hyperforce leverages this to expand its infrastructure using metadata artifacts (terraform manifests), which are kept under source control to maintain any unwanted vulnerability introduction, and process adherence.
Multi-Availability-Zone
To guarantee high availability, Hyperforce leverages the multiple availability zones in public clouds, which ensures that the compute resources are deployed across multiple regions which are close enough in physical proximity to act as a single system, while yielding the reliability of distributed systems.
Zero Trust
Hyper force is a zero-trust architecture – that means, no implicit access to resources in the system is provided. All data is encrypted at all times while at rest or during transfer. All request paths are explicitly authenticated and authorized. By employing the principle of least privilege access to operators is provided just in time with automated time bound access removal process.
Migration To Hyperforce
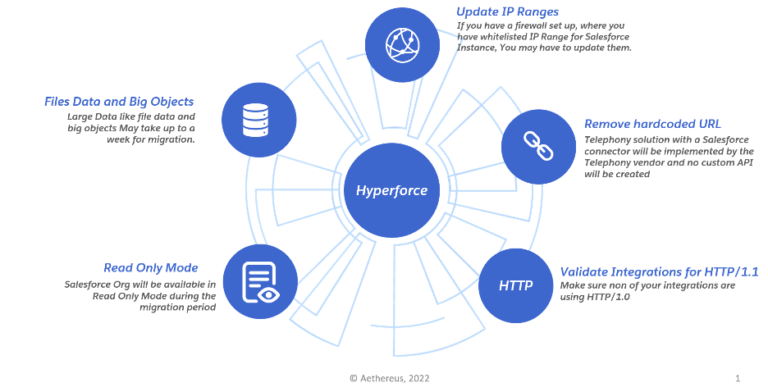
If you are planning a migration to Hyperforce, then here are our top 5 considerations that you should watch out for:
- Only production instance will get migrated to Hyperforce, if you have multiple sandbox instances then they will have to be re-created or refreshed post migration.
- Read Only Instance During the process of migration, the Salesforce org will be accessible only in read only mode. Make sure that all the integrations with Salesforce are paused for the migration period and retry mechanisms are in place.
- Remove any hardcoded references to Instance URL– If there are any stored Salesforce urls then make sure that they are not the instance URLs like na1.salesforce.com, ap15.salesforce.com, cs110.salesforce.com. As a best practice its always advised to enable My Domain in the org and use my domain URLs.
- Update allowed IP list ranges – If there is a network firewall in place which blocks incoming requests based on the IP ranges then ensure that IP ranges are updated to include the new Hyperforce cloud ranges.
- Make sure that HTTP/1.1 is used across all integrations. As Hyperforce does not support HTTP/1.0 requests, this becomes important if there are integrations between salesforce and legacy systems which use HTTP/1.0

